AI for Cyber Defense:
Ready to Entrust
Your Business to a Machine?
AI and cybersecurity make a powerful team that gives businesses better protection than ever before, though it comes with its own set of challenges. The digital world has seen AI reshape the scene of business operations. It streamlines processes, makes decision-making better, and improves cybersecurity measures by a lot.
The benefits are clear, but businesses need to think over the risks of AI before they hand over control to machines. AI-powered cybersecurity tools can process massive data sets, spot threats, and fight back against attacks right away. This proactive shield catches and stops threats before any damage occurs. UK employers have noticed the change - 35% of them say improved productivity tops the list of AI benefits.
But AI in cybersecurity cuts both ways. Criminals now use AI to make their attacks stronger and steal business data. This has sparked a tech arms race. Smart AI implementation spots network issues better than old methods ever could. Businesses can now tackle threats faster and with pinpoint accuracy.
This piece shows you how to tap into the benefits of AI in cybersecurity while dodging its risks. You'll learn about immediate threat detection, streamlined operations, weak spots to watch for, and smart ways to bring AI into your cyber defense setup.
The Business Case for AI in Cyber Defense
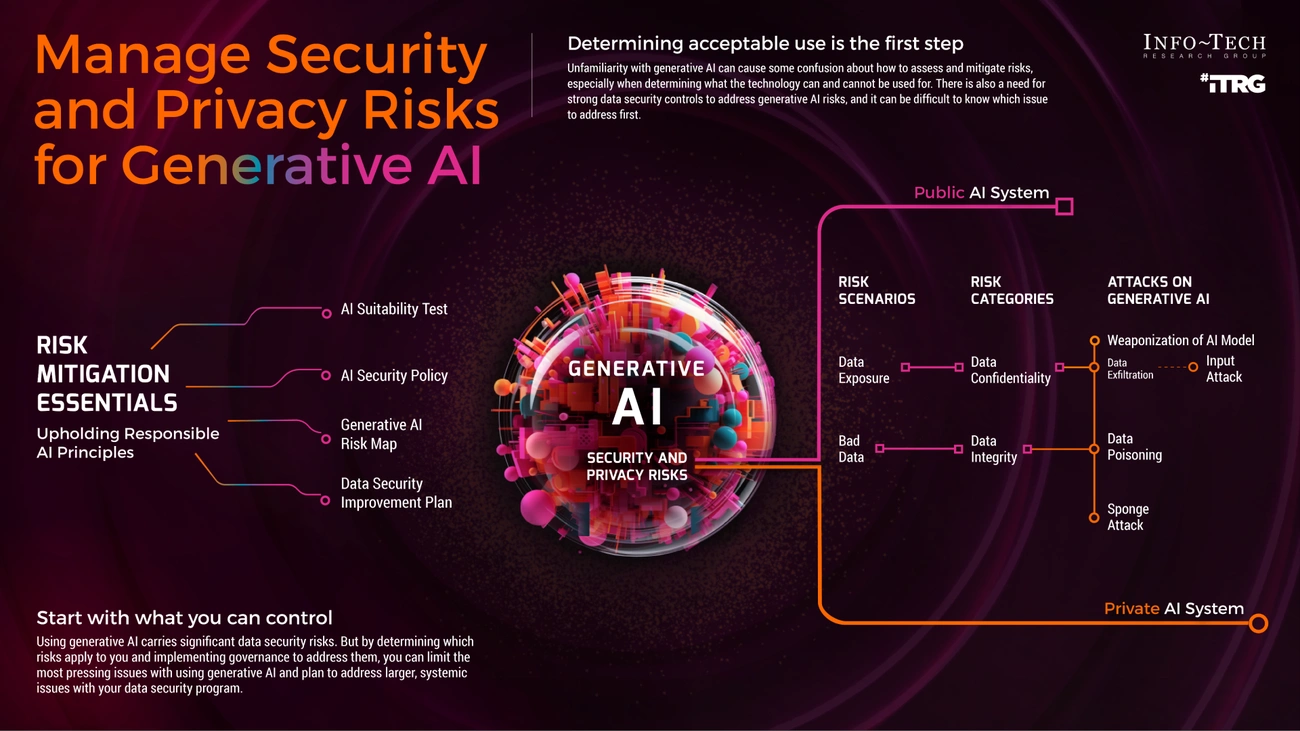
Image Source: AI Business
Organizations now invest heavily in AI-powered cybersecurity. Global spending has reached USD 24 billion in 2023 and will likely surge to USD 133 billion by 2030. This growth shows why businesses are racing to integrate AI into their cyber defense strategies.
AI for up-to-the-minute threat detection
Identifying threats before damage occurs is crucial for effective cybersecurity. AI stands out at monitoring and recognizing patterns. It analyzes big amounts of data to spot anomalies that humans might miss. These systems learn normal behavior patterns of users and devices. They quickly flag any changes that could signal attacks like cloud account theft or unauthorized entry.
AI-powered threat detection goes beyond known threats. It spots new attack patterns through unsupervised learning. Security teams can now detect emerging threats before human analysts even know about these tactics. AI algorithms can take apart malware, spot unusual logins, and predict weak points based on past data.
Boosting operational efficiency with automation
AI proves its worth beyond just detecting threats. Studies show 74% of leaders report AI delivers ROI in the first year. Companies that use security AI and automation extensively save USD 2.2 million in breach costs compared to those that don't.
AI-driven automation changes how companies use their resources. It handles routine work like system checks and compliance monitoring. This lets security experts focus on complex threats where human judgment matters most. Google Cloud AI's analysis showed a 727% three-year ROI with about 8-month payback for AI projects.
Enhancing fraud detection and prevention
Banks and financial firms benefit greatly from AI-powered fraud detection. Machine learning models study transaction patterns and give risk scores based on amount, location, and past actions. These systems can spot suspicious patterns that humans miss—like similar money movements between scattered accounts that might signal money laundering.
AI helps detect fraud earlier in the attack cycle. This minimizes damage and stops breaches that traditional methods might miss. The technology adapts to new fraud tactics and protects against evolving threats while keeping operations smooth.
Understanding the Risks of AI in Cybersecurity

Image Source: Info-Tech Research Group
AI brings powerful cybersecurity capabilities, but businesses need to think over the risks carefully before deploying it. Traditional practices don't deal very well with the complex security challenges that come with rapid AI adoption.
Data privacy and compliance challenges
AI-driven security systems need massive datasets that often contain sensitive information, despite their benefits. These AI models might expose confidential data unintentionally through various ways. A good example shows how ChatGPT accidentally revealed some users' conversation histories to others. Malicious actors can also extract sensitive details through model inversion attacks. These attacks help them figure out personal data about people in the training dataset.
Companies must guide their way through complex regulations. AI systems that handle personal data need to follow GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS rules. The challenge grows when AI extracts meaning beyond the data's original purpose, which might break purpose limitation principles.
AI-powered cyberattacks and adversarial threats
Bad actors now employ AI to boost their attack capabilities in several worrying ways:
- Advanced attack automation: AI speeds up cyberattacks, with breakout times now often under an hour.
- Sophisticated phishing: AI creates highly customized and convincing emails that get past traditional detection methods.
- Polymorphic malware: AI-generated malware changes itself immediately, making it hard for regular security tools to catch.
Adversarial AI is a new threat where attackers fool AI systems by making subtle input changes that trick models into wrong decisions. These attacks are particularly dangerous because they leave no traces in logs and don't trigger obvious warnings.
Over-reliance on automation and false positives
Trusting AI-powered security too much creates weak spots. IBM reports that organizations get about 11,000 security alerts daily, with up to 70% being false alarms. This "alert fatigue" makes security teams less sensitive and they might miss real threats.
Security analysts use about 25% of their time checking false positives. This adds up to roughly 1,300 hours yearly and costs organizations around £1.11 million annually. Beyond money losses, too much trust in AI creates a false sense of safety. These systems might miss subtle or new threats they haven't seen before.
How to Safely Entrust Your Business to AI
AI cybersecurity needs a well-laid-out approach to handle both opportunities and risks. The World Economic Forum shows that only 37% of organizations have processes to check AI security before deployment. Yet 66% expect AI to substantially affect cybersecurity within a year.
Building a risk management framework
A strong AI risk management framework helps identify and reduce potential negative effects. NIST's AI Risk Management Framework offers a voluntary but complete structure to build trustworthy AI systems. This framework helps teams document and handle risks better, which creates more reliable AI systems. Companies should blend AI risk planning into their main risk management strategies instead of handling them separately.
Choosing secure and compliant AI tools
Companies need a full picture of their AI security providers' safety measures. Security teams must apply zero trust network principles to AI systems. They should put approved large language models behind single sign-on identity platforms with multifactor authentication. AI tools should improve team productivity without disrupting existing processes.
Training employees on AI usage and risks
Human error leads to many cybersecurity breaches, so proper training programs matter. SmartAwareness offers programs in multiple languages. These include phishing simulations and resources that help build secure habits to protect personal and company data. Each employee needs different levels of AI security knowledge based on their role.
Establishing clear AI governance policies
Good governance starts with an AI ethics committee that develops and enforces the framework. Teams must set up tracking and logging systems to record when AI models get trained, retrained, and generate responses. Different departments should work together to create standards that protect both technical and ethical aspects of AI.
Getting Started with AI in Your Cyber Strategy
A methodical approach that balances ambition with pragmatism is essential when adding AI to your cybersecurity strategy. Organizations achieve success through a structured path that maximizes benefits and minimizes disruption.
Start small with high-impact use cases
Your team should identify specific areas where AI can deliver immediate value. Critical functions like threat detection and response allow AI to analyze big datasets quickly and identify potential threats. Quick wins that showcase AI's effectiveness emerge when organizations target these high-value scenarios. AI shows its strength when it analyzes user authentication data, detects anomalies, and triggers additional verification as needed.
Integrate AI with existing security systems
Middleware serves as a reliable connector between older frameworks and new AI technologies, which eliminates the need for complete system overhauls. Most AI platforms come with APIs or connectors that simplify linkage with other cybersecurity resources. This blend improves existing tools' capabilities and enables more sophisticated threat detection without disruptions.
Monitor and adapt AI models continuously
AI systems need regular assessment to perform as intended. System monitoring spots anomalies or inefficiencies while algorithm fine-tuning adapts to the changing cybersecurity world. AI's core strength comes from learning new data patterns, which makes it fluent in detecting zero-day threats through ongoing refinement.
Conclusion
AI cybersecurity offers amazing chances but also creates big challenges for modern businesses. AI has changed how we detect threats with up-to-the-minute analysis and makes operations much more efficient. Companies save millions in potential breach costs when they use AI, and they often see returns within their first year.
All the same, these benefits come with major risks. Data privacy issues, AI-powered attacks, and too much reliance on automation create weak spots that businesses need to fix right away. Security teams still struggle with false positives that waste resources and might hide real threats.
Success with AI needs a balanced approach. Companies should create complete risk management frameworks that work with standards like NIST and choose secure, compliant tools carefully. Human error leads to many security breaches, so staff training remains crucial.
The best way forward starts with small but powerful changes instead of complete overhauls. New systems work best when they fit with your existing security setup, which protects you better with minimal disruption. AI models need constant watching and updates to keep up with new threats.
We can't simply answer whether businesses should trust machines with their security. The real answer lies in smart implementation that combines AI's strengths with human oversight. AI definitely makes cybersecurity better, but organizations must use it wisely and understand what it can and can't do. Companies that find this sweet spot will without doubt build stronger defenses against sophisticated cyber threats while they retain control of their security strategy.
